Share of main export partners of China 2023
In 2023, the European Union countries imported approximately 14.8 percent of the Chinese export volume. In that year, ASEAN was the largest Chinese merchandise importer.
China’s economic prosperity has been closely related to its status as the world’s factory. For about a decade between 2005 and 2015, exports contributed more than 20 percent to China’s gross domestic product. However, the share of exports to GDP contribution is currently on the decline. Nonetheless, China maintains a trade surplus of about 823 billion U.S. dollars and remains first among countries with the highest trade surplus worldwide as of 2023. While China displays high growth potential for service exports such as tourism, transportation, banking and financial services, as well as insurance and education services, the main focus of China’s export industry remains merchandise. In 2022, Chinese merchandise exports made up 14.4 percent of all global exports, whereas service based exports contributed only six percent.
In terms of most exported merchandise categories, food and live animals used for food were the main primary goods. Among the manufactured goods, automatic data processing machines, clothing, smartphones, and integrated circuits were the categories with the highest export value in China in 2023.
Distribution of Chinese exports
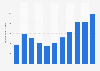
In 2023, China exported goods with a total value of around 23.8 trillion yuan and imported goods with a value of 18 trillion yuan. That year, China ranked second among the countries with the largest gross domestic product, following the United States.China’s economic prosperity has been closely related to its status as the world’s factory. For about a decade between 2005 and 2015, exports contributed more than 20 percent to China’s gross domestic product. However, the share of exports to GDP contribution is currently on the decline. Nonetheless, China maintains a trade surplus of about 823 billion U.S. dollars and remains first among countries with the highest trade surplus worldwide as of 2023. While China displays high growth potential for service exports such as tourism, transportation, banking and financial services, as well as insurance and education services, the main focus of China’s export industry remains merchandise. In 2022, Chinese merchandise exports made up 14.4 percent of all global exports, whereas service based exports contributed only six percent.
In terms of most exported merchandise categories, food and live animals used for food were the main primary goods. Among the manufactured goods, automatic data processing machines, clothing, smartphones, and integrated circuits were the categories with the highest export value in China in 2023.